Introduction
The term “blockchain” has proliferated in the digital age, frequently being hailed as the technology that will transform a range of sectors, including healthcare and finance. However, what precisely is blockchain, and how does it operate? In this extensive book, we will explore the foundations of blockchain technology, including its underlying theories, workings, and practical applications.
Definition
Blockchain is a distributed database that keeps track of an ever-expanding set of organised records known as blocks. The block, a digital piece of information, stores data like the time, date, payment participants, and other specifics. A hash is a special code that is assigned to each block. If a code hash is assigned, the block is ready to be added to the blockchain. Blockchain technology has the potential to greatly benefit a wide range of industries, including retail, healthcare, and agriculture.
Understanding Blockchain
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure, transparent, and immutable manner. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity controls the ledger, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, enabling participants to transact directly with one another without the need for intermediaries.
The Anatomy of a Blockchain
A blockchain consists of three key components:
Blocks: These are the building blocks of the blockchain, containing a list of transactions that have been validated and confirmed by network participants. Each block typically includes a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain-like structure that links all blocks together.
Transactions: These are records of data exchanges between participants in the network. Transactions can represent various types of digital assets, such as cryptocurrency payments, smart contracts, or tokenized assets.
Consensus Mechanism: This is the protocol used to achieve agreement among network participants on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. Delegd Pateroof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of Work (PoW), and Proof of Stake (PoS) are common consensus procedures.
How Blockchain Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Initiation: A participant initiates a transaction by creating a digital record containing relevant information, such as the sender’s and recipient’s addresses, the amount being transferred, and any additional data.
Propagation: The transaction is broadcasted to all nodes (computers) in the network.
Verification: Nodes in the network validate the transaction by verifying its authenticity and ensuring that the sender has sufficient funds to complete the transaction.
Block Formation: Validated transactions are grouped together into a block. Miners (nodes responsible for creating new blocks) compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle, known as the “proof of work” or “proof of stake,” to add the block to the blockchain.
Consensus: Once a miner successfully solves the puzzle, the proposed block is broadcasted to the network. Other nodes in the network validate the block, and if a consensus is reached, the block is added to the blockchain.
Chain Extension: The newly added block becomes the latest link in the blockchain, and the process repeats for subsequent transactions.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for a central authority or intermediary to oversee transactions.
Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain enables all participants to view transaction history and verify the integrity of the ledger.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and security of the data.
Security: Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology to enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track and trace products throughout the supply chain, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Smart Contracts: Since the terms of these contracts are explicitly written into the code, they are self-executing. Blockchain facilitates the secure execution and enforcement of smart contracts without the need for intermediaries.
Identity Management: Blockchain-based identity solutions lower the risk of fraud and identity theft by providing a decentralised, secure method of managing digital identities.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
As blockchain continues to evolve, its potential to disrupt various industries and reshape the digital landscape is undeniable. From finance and healthcare to supply chain management and beyond. The adoption of blockchain technology is poised. To accelerate, driving innovation and transforming the way we transact, communicate, and interact in the digital age.
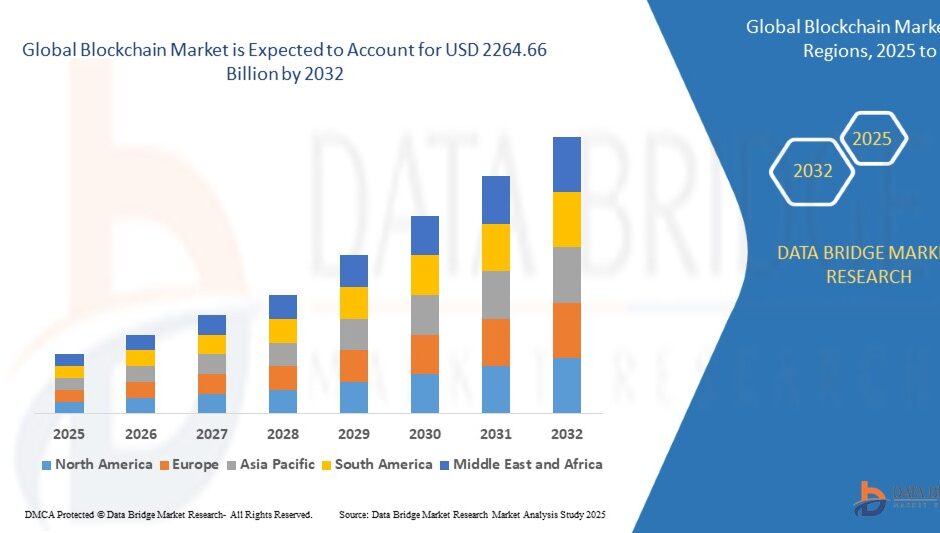
Growth Rate of Blockchain Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the worldwide blockchain market is projected to grow from its 2024 valuation of USD 29.62 billion to USD 2264.66 billion by 2032. Growth in cryptocurrencies and digital assets is expected to propel the market’s growth at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 71.96% between 2025 and 2032.
To learn more click here.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-blockchain-market
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a paradigm shift in data sharing, management, and storage. By providing a secure, transparent, and decentralized framework for transactions. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize countless industries and empower individuals worldwide. As we continue to explore the possibilities of this transformative technology, one thing is clear: the future of blockchain is bright. And its impact will be felt for years to come.